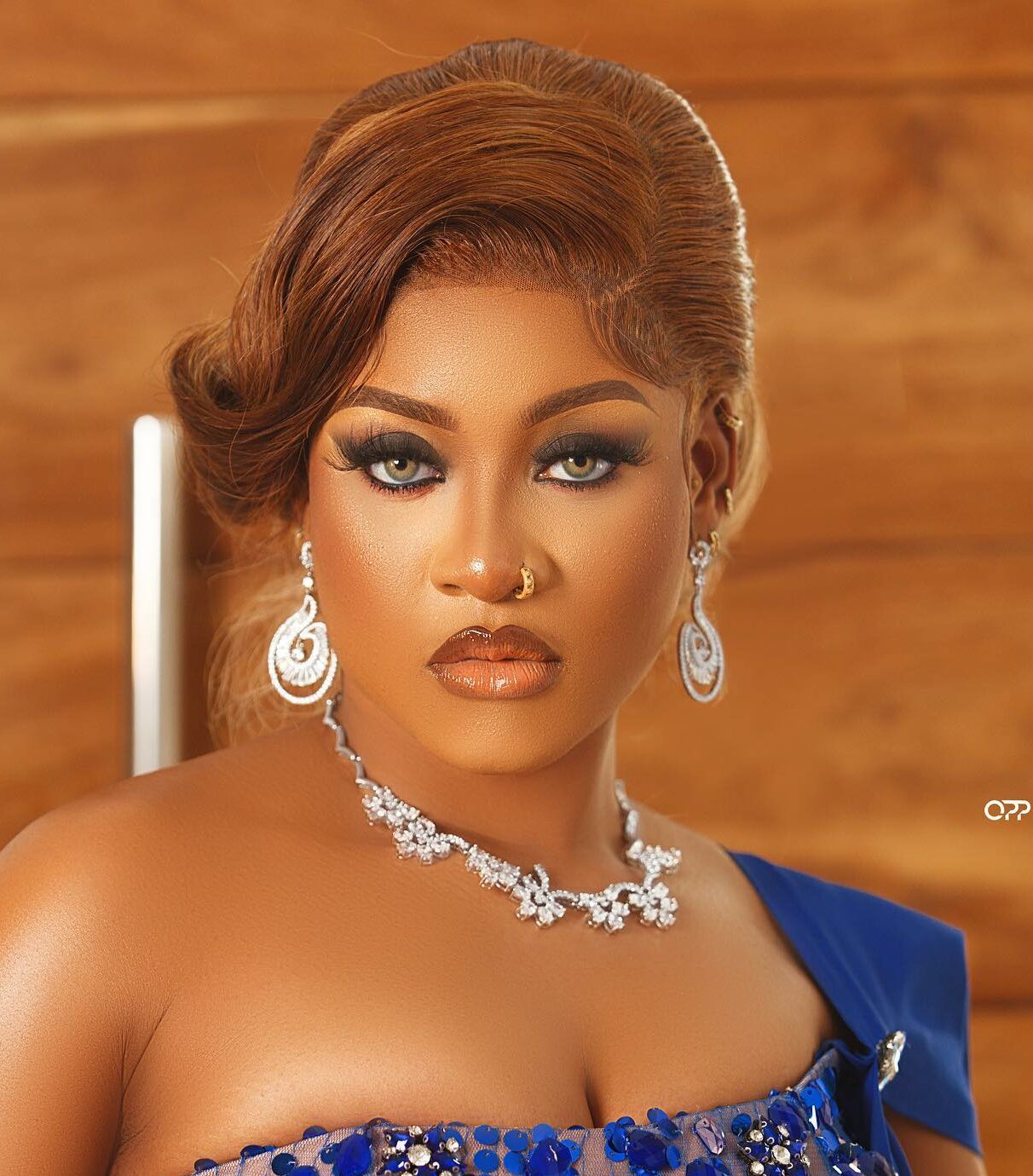
Nollywood actress Sarah Martins has formally responded to the Lagos State Government’s warning regarding her recent public cooking activity, clarifying that the event was an emotional reconnection with vulnerable children rather than a deliberate breach of environmental laws.
The response comes after the Lagos State Commissioner for the Environment and Water Resources, Tokunbo Wahab, on Saturday, cautioned the actress against cooking on public roads, warning that she risks arrest and prosecution if she continues the practice.
In an open letter posted on her Instagram handle on Sunday, Martins, the founder of the Sarah Martins Golden Heart Foundation, sought to set the record straight, stating that the meal was prepared in a controlled environment.
“I would like to respectfully clarify that I did not cook on the walkway or on the main street.
“The meal was prepared in front of the King’s Palace under the supervision of security personnel, and the activity took place very far from the main road, ensuring that it did not obstruct movement or create any public nuisance,” she wrote.
Explaining the motivation behind the act, the actress described it as a response to the pleas of street children she frequently encounters.
“The visit was simply born out of an emotional moment. I had deeply missed the bond I share with the vulnerable street children in that area,” she explained.
“As I occasionally drive past that axis, the children often plead with me to come back and cook with them like I used to. On this particular day, I decided to spend some time with them and prepare a meal, purely to reconnect and create memories with the kids who have always shown me genuine love,” she added.
The actress offered an apology to the state government for any perceived impropriety, saying, “My brief return to that location was never intended to create any form of public nuisance, but simply to share a heartfelt moment with children who have continued to ask for my presence.
“However, if my actions were perceived as inappropriate in any way, I sincerely apologide. I hold the laws and environmental standards of Lagos State in the highest regard.
“Going forward, I will ensure that all cooking activities are carried out strictly within the charity kitchen provided for the foundation.”
In her response, Martins also expressed gratitude to Seyi Tinubu, the President’s son, noting that his donation of a charity kitchen was specifically intended to ensure her feeding programs are conducted in a proper and organised environment, which she said her foundation remains committed to using.
PUNCH Online reports that Martins was arrested in October 2025 by KAI officials while she was cooking on a road median in Lekki, seizing her equipment.
The Lagos State Government defended the operation, with Wahab stating that the actress had engaged in unauthorised activities on public infrastructure in contravention of environmental and sanitation regulations.
While she previously claimed to have received ₦20 million from his office, Seyi Tinubu reportedly denied making the donation personally, saying some friends, moved by compassion, had raised funds to help her secure a proper space for her charity work, but stressed that he did not support any act that violated Lagos State laws.
punch.ng
FOLLOW US ON: