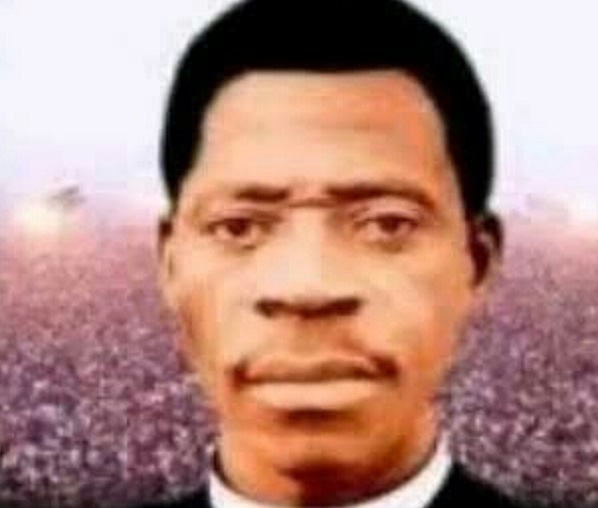
Apostle Joseph Ayodele Babalola – The Story of the Powerful Leader of the Christ Apostolic Church, popularly called CAC in Nigeria
Joseph Ayodele Babalola was born on April 25, 1904 to David Rotimi and Madam Marta Talabi who were members of the Anglican Church. The family lived at Odo-Owa in Ilofa, a small town about ninety kilometres from Ilorin in Kwara State, Nigeria. His father was the Baba Ijo (literally meaning, father of the church) of the C.M.S. Church at Odo-Owa. According to Pastor Medayese in his book, “Itan Igbe dide Woli Ayo Babalola”, mysterious circumstances surrounded the birth of Apostle Babalola. On that day, it was believed that a strange and mighty object exploded and shook the clouds
On January 18, 1914, Apostle Babalola was taken by his brother M.O. Rotimi, a Sunday school teacher in the C.M.S. Church at Ilofa, to Osogbo. Babalola started school at Ilofa and got as far as standard five at All Saints’ School, Osogbo. However, he quit school when he decided to learn a trade and became a motor mechanic apprentice. He did not continue long in this vocation before joining the Public Works Department (PWD) and he was among the road workers who constructed the road from Igbara-Oke to Ilesa, working as a steam roller driver.
Apostle Babalola was called by God into the prophetic office to stand before men. His strange experience started on the night of September 25th, 1928 when he suddenly became restless and could not sleep. This went on for a week and did not know the cause of such experience. One day when he was working on the Ilesa-Igbara-Oke road, the steam roller’s engine suddenly stopped to his utter amazement. There was no visible mechanical problem, and he became shocked. He was in this state of confusion when a great voice “like the sound of many waters” called him three times. The voice was loud and clear, telling him that he would die if he refused to heed the divine call to go into the world and preach. Babalola did not want to listen to this voice and he responded like many of the Biblical prophets, who, when they were called by God, did not normally yield to the first call. Apostle Babalola gave in only after he had received the assurance of divine guidance.
To go on the mission, he had to resign his appointment with the Public Works Department. Mr. Fergusson, the head of his unit, tried to dissuade him from resigning but Apostle Babalola was bent on going on the Lord’s mission. The same voice came to Apostle Babalola again, asking him to fast for seven days. He obeyed and at the end of the period he saw a great figure of a man who, according to Pastor Alokan, resembled Jesus. The man in a dazzling robe spoke at length about the mission he was to embark upon. The man also told him of the persecution he would face and at the same time assured him of God’s protection and victory. A hand prayer bell was given to Apostle Babalola as a symbol. He was told that the sound of the bell would always drive away evil spirits. He was also given a bottle of “life-giving water” popularly called “Omi-iye” to heal all kinds of sicknesses. Consequently, wherever and whenever he prayed into water, miracles of effective and total healing were recorded for those who drank the water. Thus, Babalola became a prophet and a man with extraordinary powers. Enabled by the power of the Holy Spirit, he could spend several weeks in prayer. Elder Abraham Owoyemi of Odo-Owa, said that the prophet regularly saw angels who delivered divine messages to him. An angel appeared in one of his prayers and forbade him to wear caps.
During one of his prayer sessions an angel appeared to him and gave him a big yam which he ordered him to eat. The angel told him that the yam was the tuber with which God fed the whole world. He further revealed that God had granted unto him the power to deliver those who were possessed of evil spirits in the world. He was directed to go first to Odo-Owa and start preaching. He was to arrive in the town on a market day, cover his body with palm fronds and disfigure himself with charcoal paints.
In October 1928, he entered the town in the manner described and was taken for a mad man. Babalola immediately started preaching and prophesying. He told the inhabitants of Odo-Owa about an impending danger if they did not repent. He was arrested and taken to the district officer at Ilorin for allegedly disturbing the town’s peace. The district officer later released him when the allegations could not be proven. However, it was said that a few days later, there was an outbreak of smallpox in the town. The man whose prophecies and messages were once rejected was quickly sought for. He went around praying for the victims and they were all healed
In March 1932, a warrant for the arrest of Babalola was issued from Ilorin in present Kwara State.
He was taken to Ilorin and then transferred to Benin City where he was charged to court.
He was sentenced to jail for six months in Benin City in March, 1932
an attempt to end the ministry of this resurging prophet who was causing some mission churches and the colonial government a great deal of concern.
Now, there was another prisoner at the Benin prison yard by the name Cyprian Ufon. Mr Ufon who hailed from Creek Town in Calabar area was very sick and depressed. Babalola prayed for him and he was healed and cured of his depression. He quickly became a follower of Babalola. Babalola later understood that he (Ufon) was the instrument of honour God had told him about during his prayer retreat at Ilofa.
Babalola electrified and turned the prison yard to a house of God. Many prisoners and warders were healed and saved.
Notably was the case of a pregnant lady, also from Creek Town who had safe delivery through the ministration of Babalola in the prison. The warders also brought their families and relatives to receive healing through the prayers of Babalola. On June 2, 1932, Pastors Idris Vaughan and George Perfect arrived in Nigeria as the first missionaries of the Apostolic Church based in Britain. They traced Babalola to Prison and paid him a visit. During the visit, the missionaries heard with their own ears what the Lord had done through Babalola in the lives of the warders and prisoners. Apostle Babalola was eventually released from prison in October, 1932 after serving his jail term.
The C.A.C. believes that the spiritual power bestowed on Babalola placed him on an equal level with Biblical apostles like Peter, Paul and others who were sent out with the authority and in the name of Jesus.
In 1930, his fame began to spread abroad most especially due to his amazing exploits at the Great Revival that happened at Ilesa which changed the spiritual climate of the western region. The impact of the great revival was felt virtually all over the country and Apostle Joseph Ayo Babalola became a force to be reckoned with in the Nigerian church. He became the leader of the pentecostal movement in Nigeria and his name was on every lip both of friends and foes, admirers and critics. Apostle Babalola however remained single and many of his family members, followers and colleagues became curious as to why he was not considering marriage being a church leader.
After persistent pressure from his father, Pa David Rotimi Talabi, Apostle Joseph Ayo Babalola got married to Dorcas on April 25, 1935. About 6000 people attended the wedding and he received a total gift of 3 pounds, 10 shillings and 6 pence. The wedding took place at the first Aladura assembly at Efon Alaaye and was conducted by Pastor David Odubanjo, Pastor J.S.B Odusona and Pastor Medaiyese. Apostle Babalola met his wife a virgin and had to give her 2 pounds and 10 shillings for the virginity, a custom of the Yoruba people at that time.
During their lifetime, Babalola used to call his wife ” Mama Abiye” and Dorcas would also call him “Baba Abiye”. They settled down in Efon Alaaye.
After a successful completion of his assignment, Apostle Joseph Ayo Babalola slept in the Lord in 1959.
Though he died several decades ago many CAC members still pray with his name. Whenever they pray they add Olorun Joseph Ayo Babalola. That is how much he is reverred by CAC adherents. He was the founder of Christ Apostolic Church (CAC).
Another noticeable feature of his work was the usage of water for healing which prompt the popular C.A.C song then: “Babalola Olomi Iye re o. Omi Iye, Iye, Iye, re o. Omi Iye…”
Tag a #CAC member.
Source:
The New People Movement
City People Magazine
Yorubaness
FOLLOW US ON:
FACEBOOK
TWITTER
PINTEREST
TIKTOK
YOUTUBE
LINKEDIN
TUMBLR
INSTAGRAM