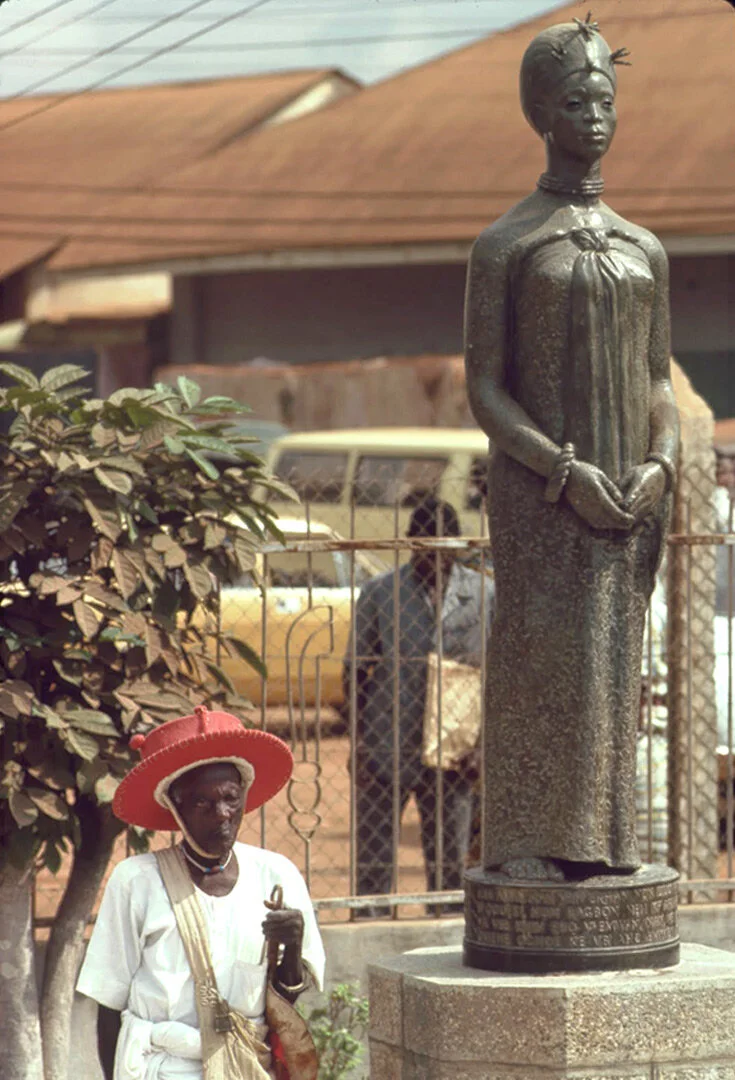
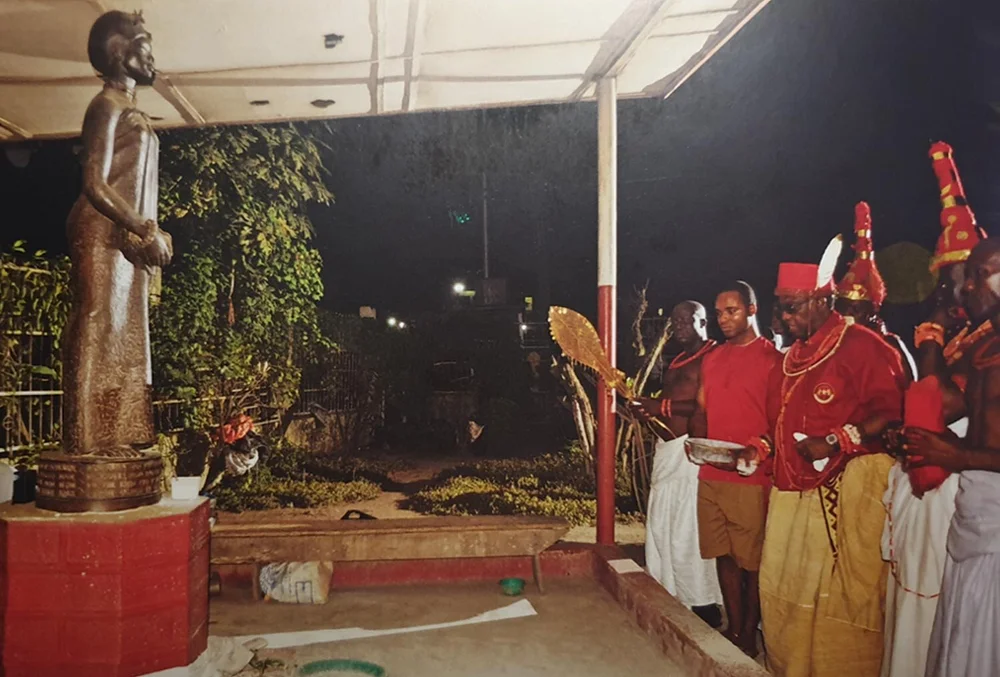
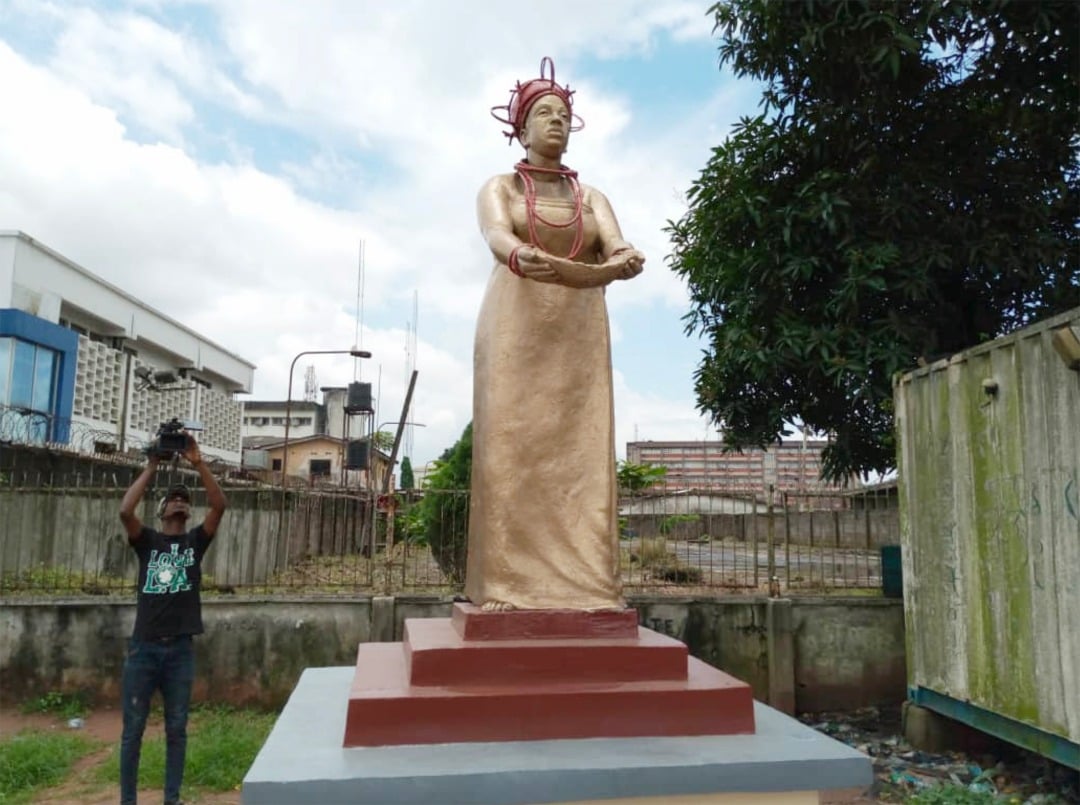
Ìwòyè-Kétu is one of the most remarkable Yoruba communities in West Africa, not only for its deep-rooted traditions but also for its unique geopolitical identity. The ancient town straddles two modern nation-states—Nigeria and the Republic of Benin—yet remains culturally, spiritually, and traditionally unified as one Yoruba settlement.
A Town Without Borders in Spirit
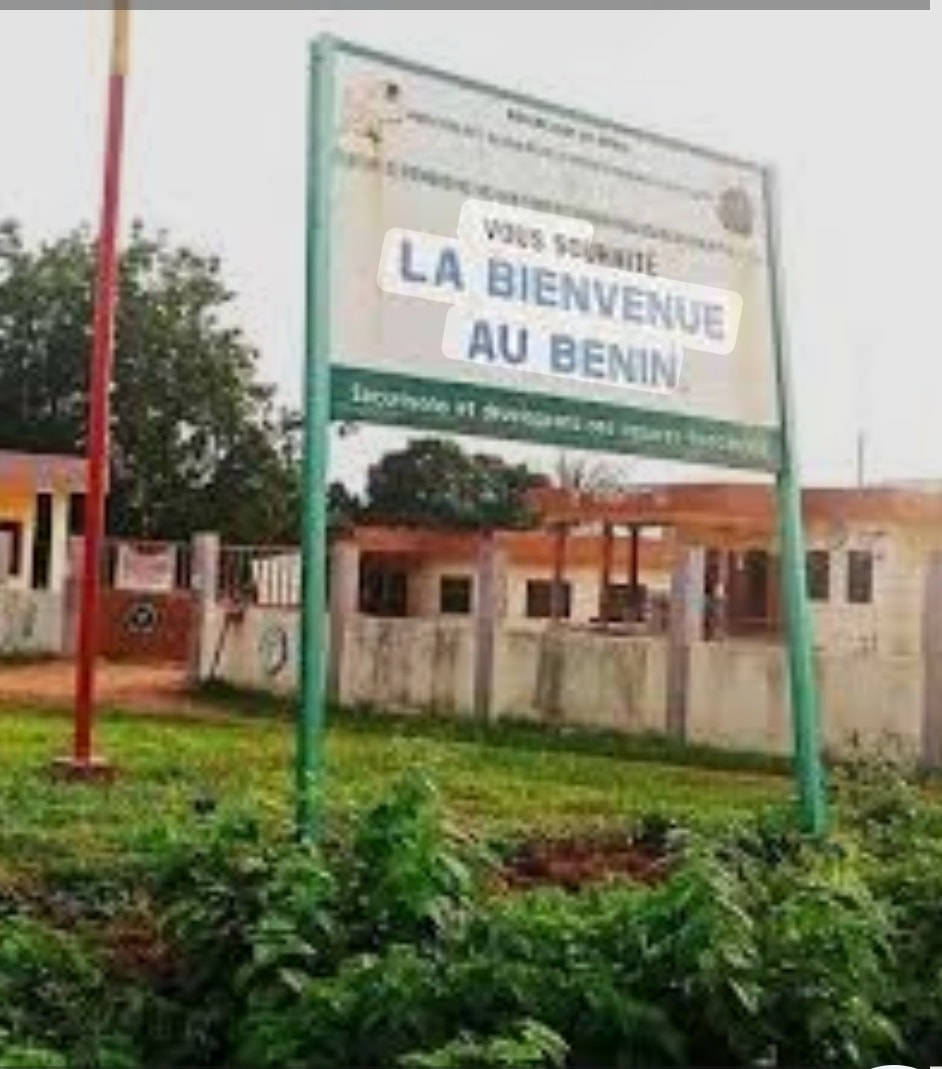
Geographically, Ìwòyè-Kétu is primarily located in Imeko/Afon Local Government Area of Ogun State, Nigeria, while its western section lies across the international boundary in the Republic of Benin. This border, imposed during the colonial partition of Africa, cuts through the town but has failed to divide its people.
Families live on both sides of the boundary, speak the same Yoruba dialect, observe the same customs, and recognise one traditional authority. Daily life reflects this dual reality: residents freely transact using both the Nigerian naira and the West African CFA franc, depending on location and convenience.
Unified Kingship Across Nigeria and Benin
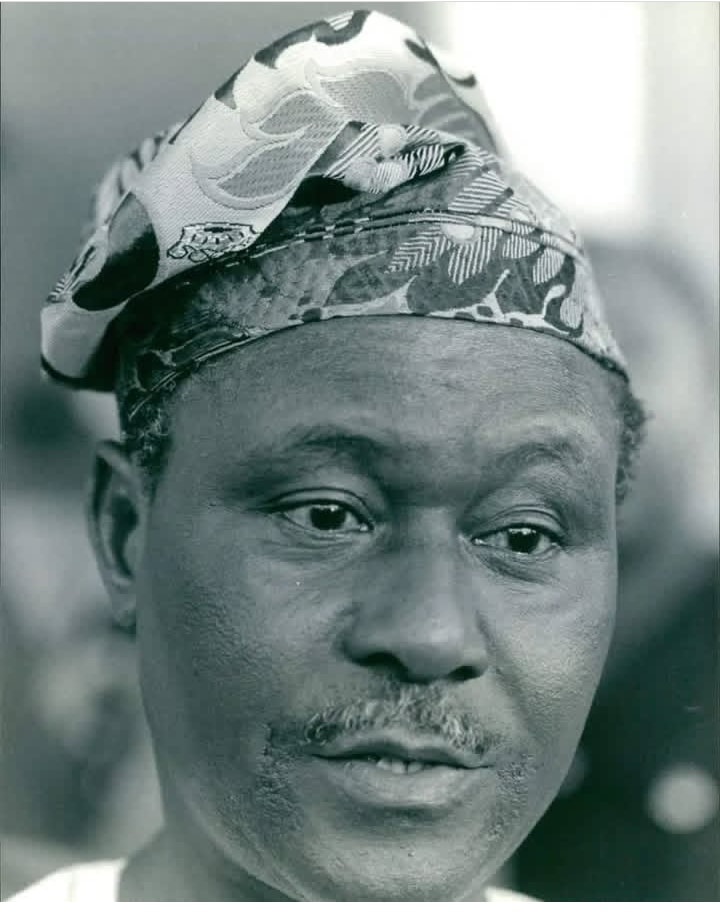
Despite existing in two countries, Ìwòyè-Kétu is governed traditionally by one paramount ruler. The recognised monarch is:
His Royal Majesty Oba (Sir) Isaac Adegbenro Oyero,
the Ooye of Ìwòyè-Kétu, also styled Adekilúrójú – Ada Páàkó II.
His authority is acknowledged by the community on both sides of the border, making Ìwòyè-Kétu a rare example of a binational Yoruba town under a single royal institution.
Origins in Ile-Ife
According to Yoruba oral tradition, Ìwòyè-Kétu was founded by Olúmu (or Olómù), a legendary migrant from Ilé-Ifẹ̀, the spiritual homeland of the Yoruba people. Like many Yoruba settlements, its founding narrative emphasises migration from Ife, reinforcing the town’s ancient roots within the broader Yoruba civilisational story.
Ìwòyè-Kétu forms part of the historic Kétu region, once a powerful Yoruba kingdom before European colonial boundaries fragmented it between British-ruled Nigeria and French-ruled Dahomey (now Benin).
Sacred Taboos That Still Govern Daily Life
Ìwòyè-Kétu is widely known for its strict traditional prohibitions, which continue to be enforced by custom and belief:
Use of umbrellas is strictly forbidden anywhere within the town.
Rearing pigs is prohibited, and pork is traditionally avoided.
In some oral accounts, digging wells is either forbidden or tightly regulated.
These taboos are believed to be tied to ancestral covenants, spiritual agreements, and the town’s founding myths. Violations are traditionally thought to invite misfortune, reinforcing collective adherence across generations.
Language, Culture, and Continuity
Despite the Nigeria–Benin divide, Ìwòyè-Kétu remains culturally seamless. Yoruba language, customs, festivals, and lineage systems are shared. The town stands at a linguistic crossroads where English and French meet administratively, but Yoruba remains dominant socially and spiritually.
A Living Example of Pre-Colonial African Unity
Ìwòyè-Kétu exemplifies how pre-colonial African societies continue to transcend modern borders. Long before Nigeria or Benin existed, the town functioned as a single cultural entity—and it still does.
In an era where borders often define identity, Ìwòyè-Kétu reminds us that history, tradition, and shared ancestry can be stronger than lines drawn on maps.
Sources
Yoruba oral traditions and local historical accounts of Ìwòyè-Kétu
Ogun State local government and cultural heritage records (Imeko/Afon LGA)
Nigerian media reports and cultural features on Ìwòyè-Kétu’s taboos and binational status
Community welcome signage and local testimonies
Cross-border Yoruba history of the Kétu Kingdom (Nigeria–Benin)
FOLLOW US ON:
FACEBOOK
TWITTER
PINTEREST
TIKTOK
YOUTUBE
LINKEDIN
TUMBLR
INSTAGRAM

 Lifestyle21 hours ago
Lifestyle21 hours ago
 News1 hour ago
News1 hour ago
 Lifestyle21 hours ago
Lifestyle21 hours ago
 Business2 hours ago
Business2 hours ago
 News18 hours ago
News18 hours ago
 Lifestyle3 hours ago
Lifestyle3 hours ago
 Crime2 hours ago
Crime2 hours ago
 Business3 hours ago
Business3 hours ago